Design patterns are proven solutions to software design problems. They help improve code quality, promote reusability, and increase maintainability. We use them to save time and produce quality, extensible and flexible code. In this article, we are going to introduce the Composite design pattern.
The Composite design pattern is a structural design pattern that allows you to combine objects in tree structures to create a hierarchy of objects. Each element of the hierarchy can itself be another hierarchy of objects. The key idea behind the composite pattern is that an object can contain other components as part of its structure, forming a tree-like structure. Each element in this hierarchy can act as another hierarchy or simply appear as a leaf in this tree.
The composite pattern consists of several key elements:
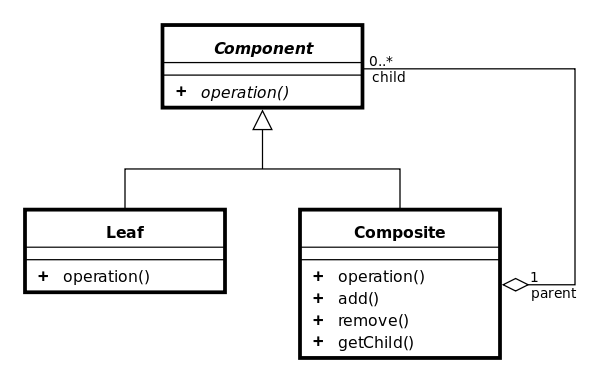
The composite pattern allows you to build complex structures while keeping the code simple and understandable. This pattern provides a similar solution for dealing with leaf or composite objects, making it easier to work with hierarchical structures.
Here is a simple example of the composite pattern in C#:
// Component
public abstract class Component
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public Component(string name)
{
Name = name;
}
public abstract void Add(Component component);
public abstract void Remove(Component component);
public abstract void Display(int depth);
}
// Leaf
public class Leaf : Component
{
public Leaf(string name) : base(name) { }
public override void Add(Component component)
{
Console.WriteLine("Cannot add to a leaf.");
}
public override void Remove(Component component)
{
Console.WriteLine("Cannot remove from a leaf.");
}
public override void Display(int depth)
{
Console.WriteLine(new string('-', depth) + " " + Name);
}
}
// Composite
public class Composite : Component
{
private List<Component> _children = new List<Component>();
public Composite(string name) : base(name) { }
public override void Add(Component component)
{
_children.Add(component);
}
public override void Remove(Component component)
{
_children.Remove(component);
}
public override void Display(int depth)
{
Console.WriteLine(new string('-', depth) + "+ " + Name);
foreach (Component component in _children)
{
component.Display(depth + 2);
}
}
}
// Client
public class Client
{
public void Main()
{
// Create a tree structure
Composite root = new Composite("Root");
root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf A"));
root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf B"));
Composite composite = new Composite("Composite X");
composite.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XA"));
composite.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XB"));
root.Add(composite);
root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf C"));
// Add and remove a leaf
Leaf leaf = new Leaf("Leaf D");
root.Add(leaf);
root.Remove(leaf);
// Recursively display tree
root.Display(1);
}
}In this example, the Component class defines common methods for leaf and composite objects. The Leaf class represents a single object in a tree structure, while the Composite class represents a composite object that can contain one or more children. The Composite class implements the common methods of the Component class and provides additional methods for managing child components, such as adding or removing them. This feature allows client code to treat leaf and composite objects uniformly, making it easy to manage object hierarchies.
To read about other design patterns, you can use the list below. There is also a code repository on GitHub that includes all the design patterns.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment