
Design patterns are proven solutions to software design problems. They help improve code quality, promote reusability, and increase maintainability. We use them to save time and produce quality, extensible and flexible code. In this article, we are going to introduce the Prototype design pattern.
The Prototype pattern is a creational pattern that allows you to create a new object from an existing object. The new object copies all the values in the original object.
The prototype pattern includes the following elements:
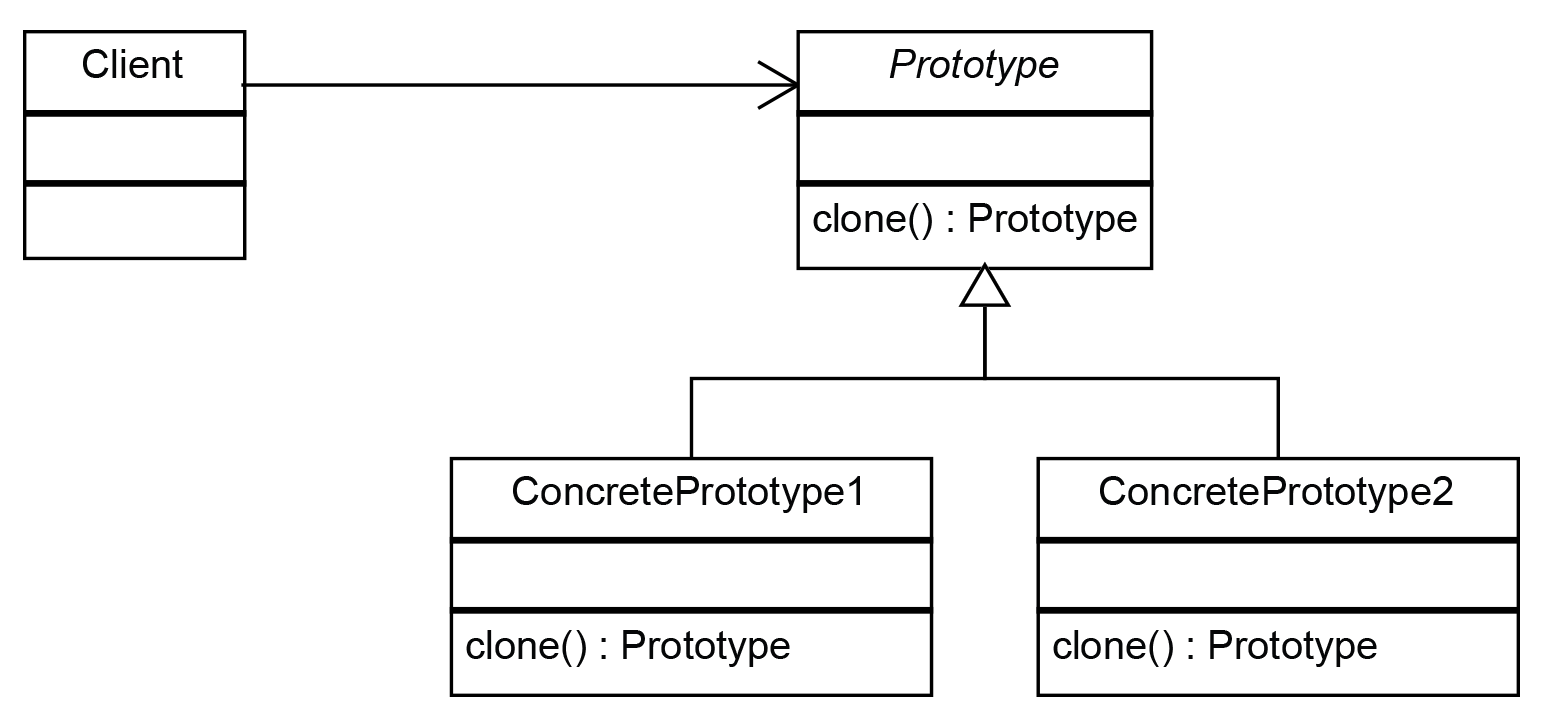
The main purpose of the prototype pattern is to create a new object without the need to create an object from scratch, and only by copying an existing object, a new object is created. Using this pattern is very useful when creating objects is expensive or the creation of an object requires complex requirements.
Below is an example of a prototype pattern in C# language:
public interface IPrototype
{
IPrototype Clone();
}
public class ConcretePrototypeA : IPrototype
{
private string _name;
public ConcretePrototypeA(string name)
{
_name = name;
}
public IPrototype Clone()
{
return new ConcretePrototypeA(_name);
}
}
public class Client
{
private IPrototype _prototype;
public Client(IPrototype prototype)
{
_prototype = prototype;
}
public IPrototype CreatePrototype()
{
return _prototype.Clone();
}
}In this example, the IPrototype interface defines the Clone method, which is used to create a copy of an existing object. The ConcretePrototypeA class implements the IPrototype interface and defines the clone method. The Client class has used this possibility to create a copy of an existing object.
To create a new object using the prototype pattern, we must first have a prototype and then create a new instance of the existing object using the Clone method.
In Photoshop, each image layer can contain different elements such as shapes, text or images. When creating a new layer, the user can copy an existing layer and modify it. The prototype pattern can be used to clone an existing layer, so that a new layer is created with the same contents as the existing layer, but can be modified independently.
In this example, the Layer class represents the prototype interface that defines the Clone method to create copies of layers. The ImageLayer and TextLayer classes are the classes that implement the Layer Interface and define the Clone method to create copies of layers.
public interface Layer
{
void AddContent(object content);
Layer Clone();
}
public class ImageLayer : Layer
{
private List<object> _content = new List<object>();
public void AddContent(object content)
{
_content.Add(content);
}
public Layer Clone()
{
ImageLayer clonedLayer = new ImageLayer();
clonedLayer._content = new List<object>(_content);
return clonedLayer;
}
}
public class TextLayer : Layer
{
private List<object> _content = new List<object>();
public void AddContent(object content)
{
_content.Add(content);
}
public Layer Clone()
{
TextLayer clonedLayer = new TextLayer();
clonedLayer._content = new List<object>(_content);
return clonedLayer;
}
}To use the prototype pattern to clone layers, you must create an instance of a layer object and then use the Clone method to create a new instance of the layer.
var originalLayer = new ImageLayer();
originalLayer.AddContent(new Bitmap("image.jpg"));
var clonedLayer = originalLayer.Clone();
clonedLayer.AddContent(new Bitmap("logo.png"));In this example, the originalLayer object is created as the initial layer. Then a new layer is created using the Clone method. The clonedLayer can be modified independently of the originalLayer.
To read about other design patterns, you can use the list below. There is also a code repository on GitHub that includes all the design patterns.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment