Event-driven architecture is a software design pattern that uses events to determine the flow of data in an application. Events can be user actions, system alerts, or any other type of event that triggers an action in the application.
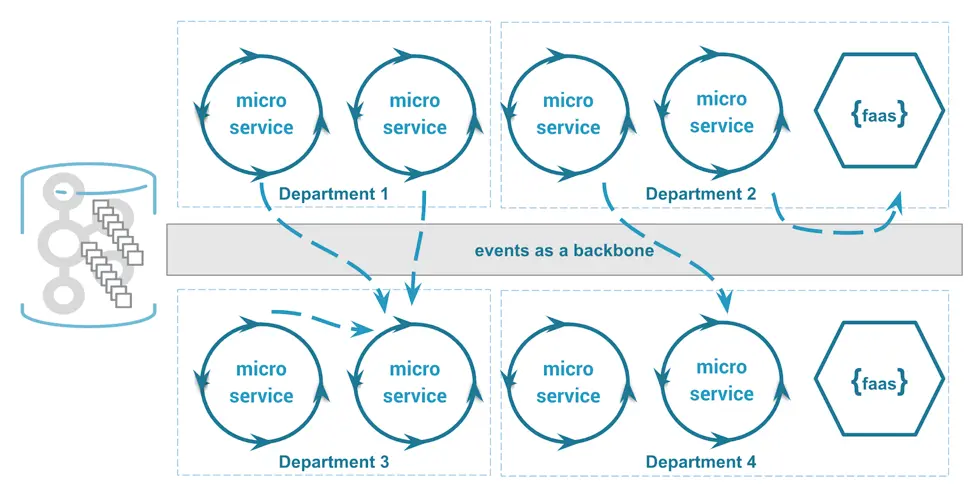
In an event-driven architecture, applications are divided into smaller, independent components called services. Each service is designed to perform a specific task and communicates with other services through events. When an event occurs, the service responsible for processing that event is notified and takes the necessary action.
Event-driven architecture has many advantages over traditional and centralized architectures. Some of its key features are introduced below.
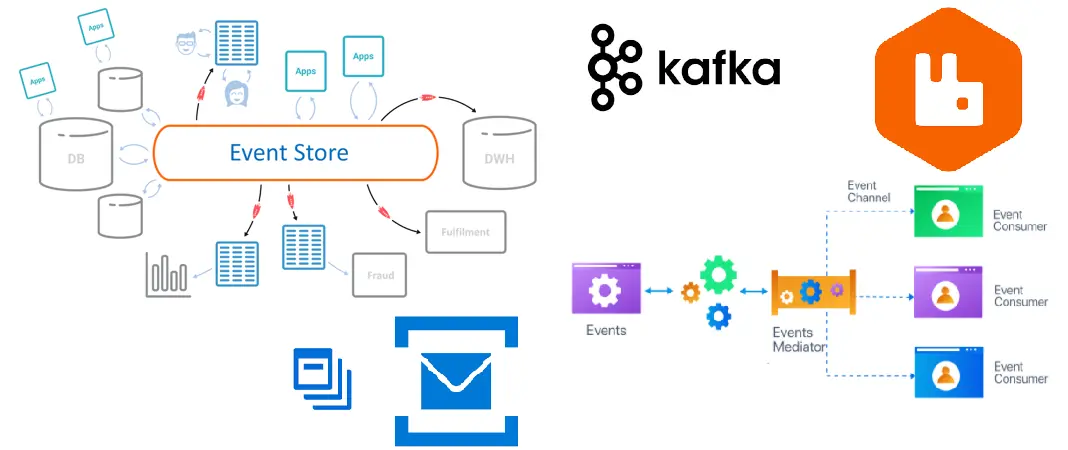
Choosing the right event streaming platform: Event-driven architectures rely on an event streaming platform to manage events. When choosing an event streaming platform, it is important to consider factors such as scalability, reliability, and ease of use.
Designing services with a specific purpose: Every service in event-driven architecture must have a specific purpose and be designed to perform a specific task. Clarity of service goals helps ensure that services do not include unnecessary functionality and that the architecture remains flexible.
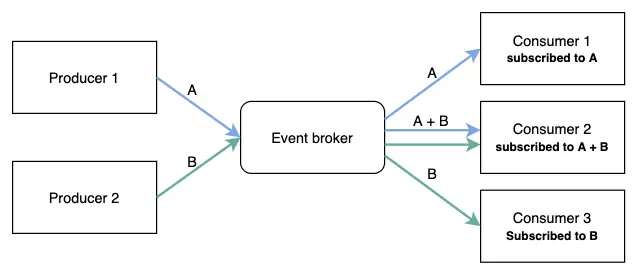
Use of asynchronous communication: Asynchronous communication is one of the key features of event-driven architecture. Using asynchronous communication, services can operate independently of each other and do not need to wait for the response of other services. Message brokers can be used to implement asynchronous communication.
Implement error handling: Since services operate independently of each other in an event-driven architecture, it is important to implement error handling to ensure that a failure in one service does not affect the entire system.
Monitoring and analyzing events: Event-driven architectures generate large volumes of events. To ensure that the system is performing as expected, it is important to monitor and analyze events.
Event-driven architecture is used in a wide variety of applications, from e-commerce platforms to financial trading systems. Here are some real examples of event-driven architecture:
Uber: Uber uses an event-driven architecture to power its real-time ride-hailing platform. Events such as taxi requests, driver availability and GPS data are used to match passengers with drivers in real time.
Netflix: Netflix uses an event-driven architecture to power its recommendation engine. Events such as user viewing history, search history and user feedback are used to create personalized recommendations for each user.
Amazon: Amazon uses an event-driven architecture to power its store platform. Events such as user search history, product visits, and purchase history are used to generate new offers and improve search results.
Airbnb: The Airbnb platform uses an event-driven architecture to enhance its user experience. When a user searches for an accommodation, events are generated to identify available accommodation and filter results based on the user's search criteria. When a user books a property, events are generated to track the booking status such as check-in and check-out times.
Event-driven architecture is a powerful software design pattern that has many advantages over traditional, centralized architectures. Event-driven architecture is very scalable and flexible and helps to increase management and create more control over system components.
When implementing an event-driven architecture, it is necessary to pay attention to things such as choosing the appropriate event flow platform, designing services with a specific purpose, using asynchronous communication, implementing error management, and monitoring and analyzing events. With the right approach, event-driven architecture can be used to power real-time applications and improve the user experience for a wide range of cases.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment