Event sourcing is a software architecture pattern that has gained popularity in recent years, especially in the field of distributed systems. This pattern involves recording every change or event that occurs in a system, unlike normal systems that only keep the latest state of the system. By storing a hierarchy of events, event sourcing enables the system to be rebuilt at any point in its history, providing a complete audit trail of every change that has occurred.
Event sourcing is an approach to record all changes in a system. These events represent changes that occur in the state of a system. With each change of status in the system, the related report is stored in an event log or database. Instead of storing the current state of the system, event sourcing records the sequence of events that led to the current state.
Event sourcing provides a complete audit trail of all changes that have occurred in the system. This makes it easy to debug and analyze the system.
Event sourcing allows the system to be rebuilt at any point in its history, making it easier to roll back and test different scenarios.
Another key benefit of event sourcing is its flexibility. Since events are stored separately from the current state of the system, it is possible to replay events in a different order or with different logic.
Considering that events are recorded based on system entities, event sourcing will be an approach that conforms to the principles of Domain-driven design(DDD). This approach makes it easier to reason about the system and the behavior of the entities and helps to align the system with business needs.
While event sourcing offers many benefits, it also has challenges to consider. One challenge is that event sourcing can lead to a higher degree of complexity in the system. Because it needs more processing infrastructure to manage events and process them. Additionally, event sourcing can require more storage space as events accumulate over time.
Another challenge is that event sourcing will require significant changes in the way data is modeled and stored. Because events are stored separately from system state, it may be necessary to create additional data structures to manage events and their relationships to system state.
Event sourcing is suitable in distributed systems that require high flexibility. In a distributed system, events can be logged and processed in multiple locations, allowing for redundancy and fault tolerance.
To implement event sourcing in a distributed system, it is important to consider how events are captured, stored, and processed. To optimally design an event sourcing system, the event log or event database must be highly available and scalable.
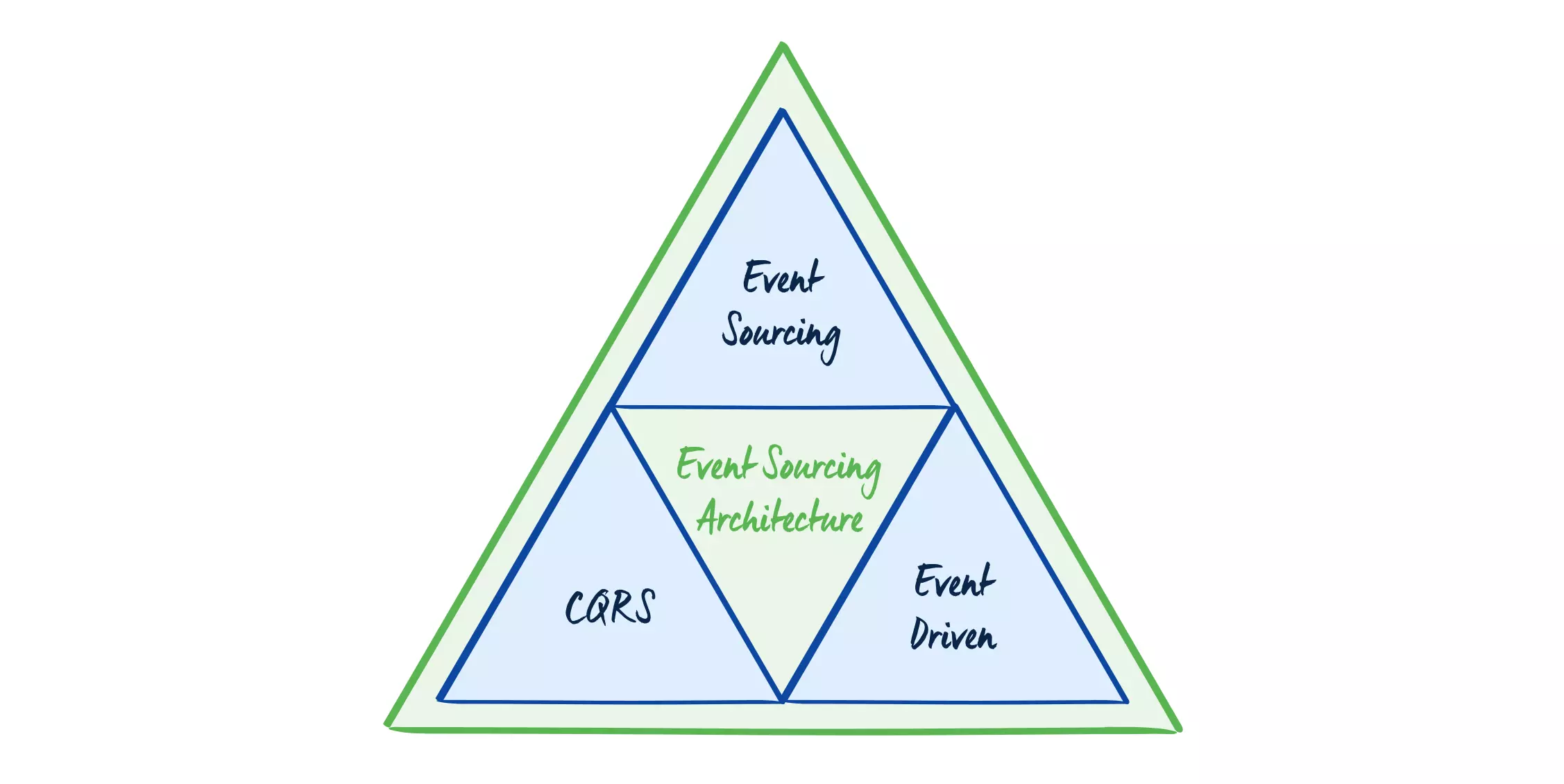
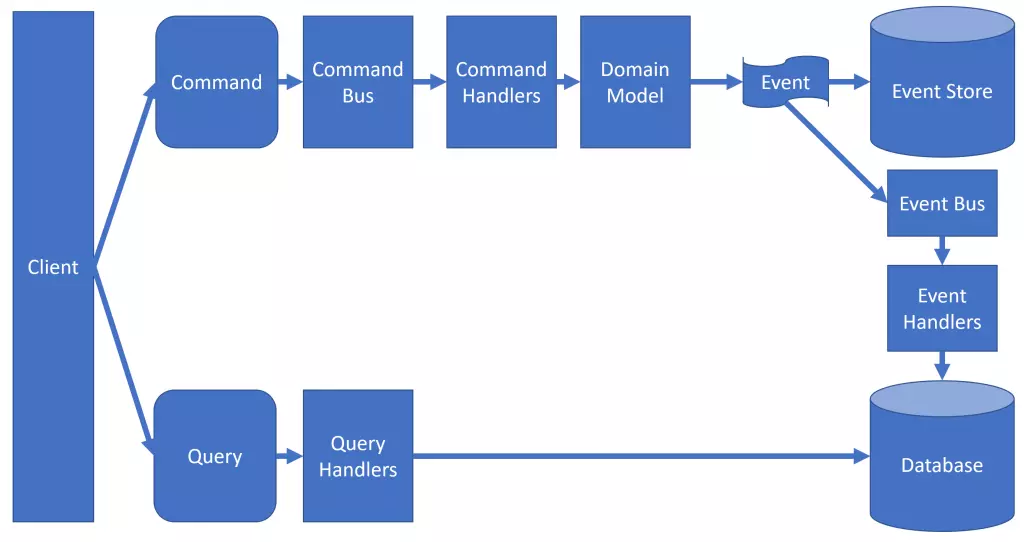
Additionally, event sourcing may need to be used in combination with other patterns, such as Command and Query Responsibility Segregation(CQRS) and Event-driven architecture (EDA), to ensure system scalability and responsiveness.
One way to implement event sourcing in a distributed system is to use a message broker, such as Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ, to capture and distribute events. This method is suitable when our system is designed with microservice architecture. Because events must be collected and stored from different services.
Another method is to use a distributed database, such as Apache Cassandra or CockroachDB, to store event history. In this approach, events are stored in a distributed manner, providing high availability and scalability.
Regardless of the implementation method, it is important to consider the impact that event sourcing will have on the overall system architecture. The increased complexity and storage requirements of event sourcing must be weighed against its potential benefits in order to make the right decision regarding the use of this approach.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment