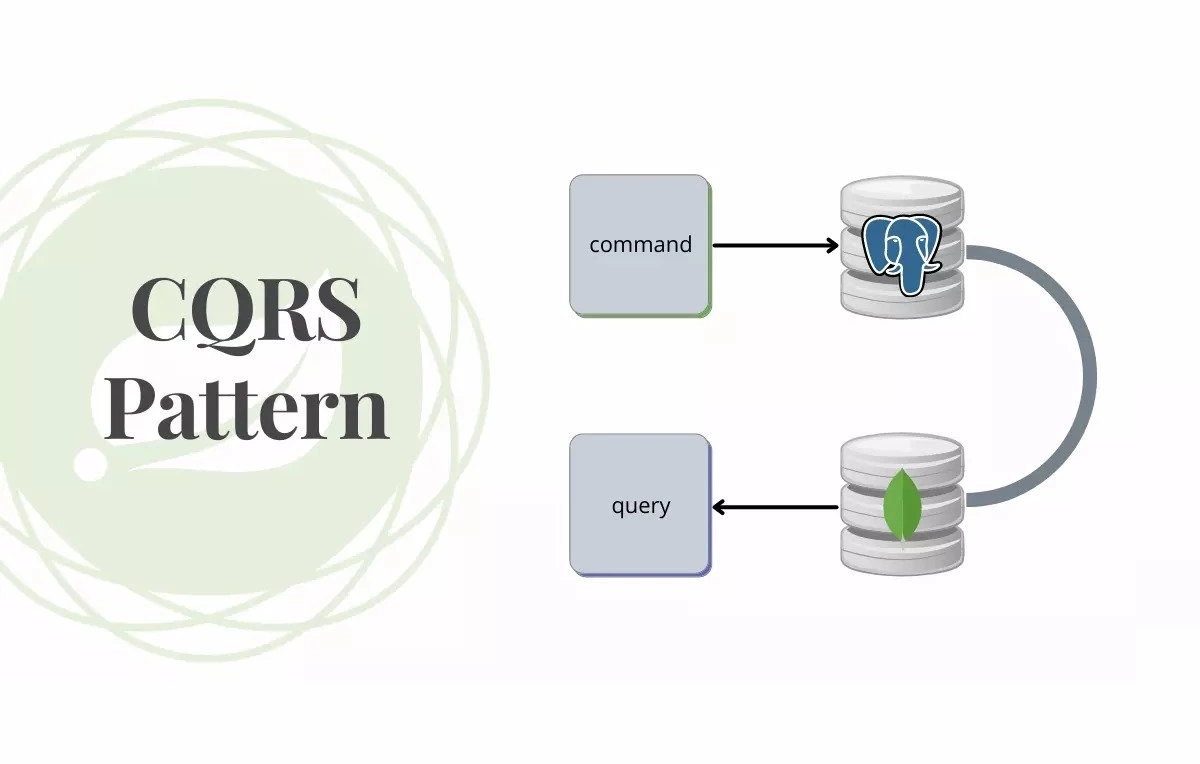
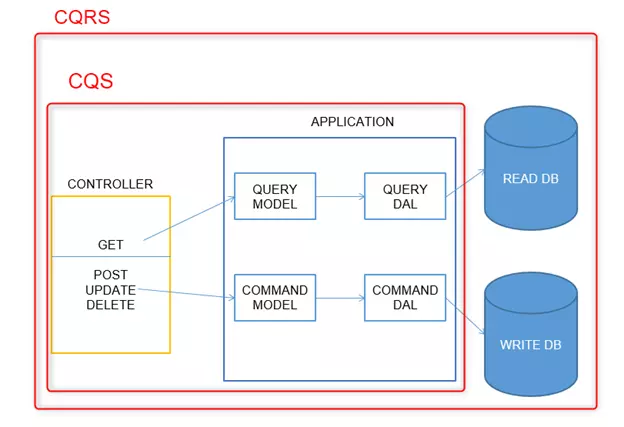
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) is a software architecture design pattern that separates the read and write operations of the program into two separate models. This pattern was introduced by Greg Young in 2010 and has since been used to simplify complex applications. Today, this approach has gained wide popularity among developers.
The main idea behind CQRS is that read and write operations of a program should be handled separately. By separating these operations into two distinct models, developers can optimize performance, simplify application architecture, and improve overall scalability.
Using CQRS has advantages that can be mentioned as follows:
Architecture Simplification: Separation of read and write operations into separate models simplifies the overall architecture of the application. This makes it easier to understand and maintain, especially for larger and more complex applications.
Optimized data storage and retrieval mechanisms: Since read and write operations have different requirements, the program can optimize its data storage and retrieval mechanisms accordingly. This can lead to faster and more efficient data processing, which can be especially useful in applications that process large amounts of data.
Improved scalability: CQRS enables independent scaling of read and write segments. Despite this feature, the read or write performance can be changed independently based on the needs of the project.
CQRS implementation can also pose challenges. Using this method will require a deep understanding of the architecture and infrastructure of the application deployment. Also, understanding the requirments of the project are influential in the correct implementation of this model, and developers should carefully check how these two models will interact with each other and how the data will be synchronized between them.
Another challenge of CQRS is that the duration of project design and modeling increases. Developers should carefully consider the data requirements of the application and design the read and write models accordingly. This can be a time-consuming and complex process, especially for applications with complex data structures.
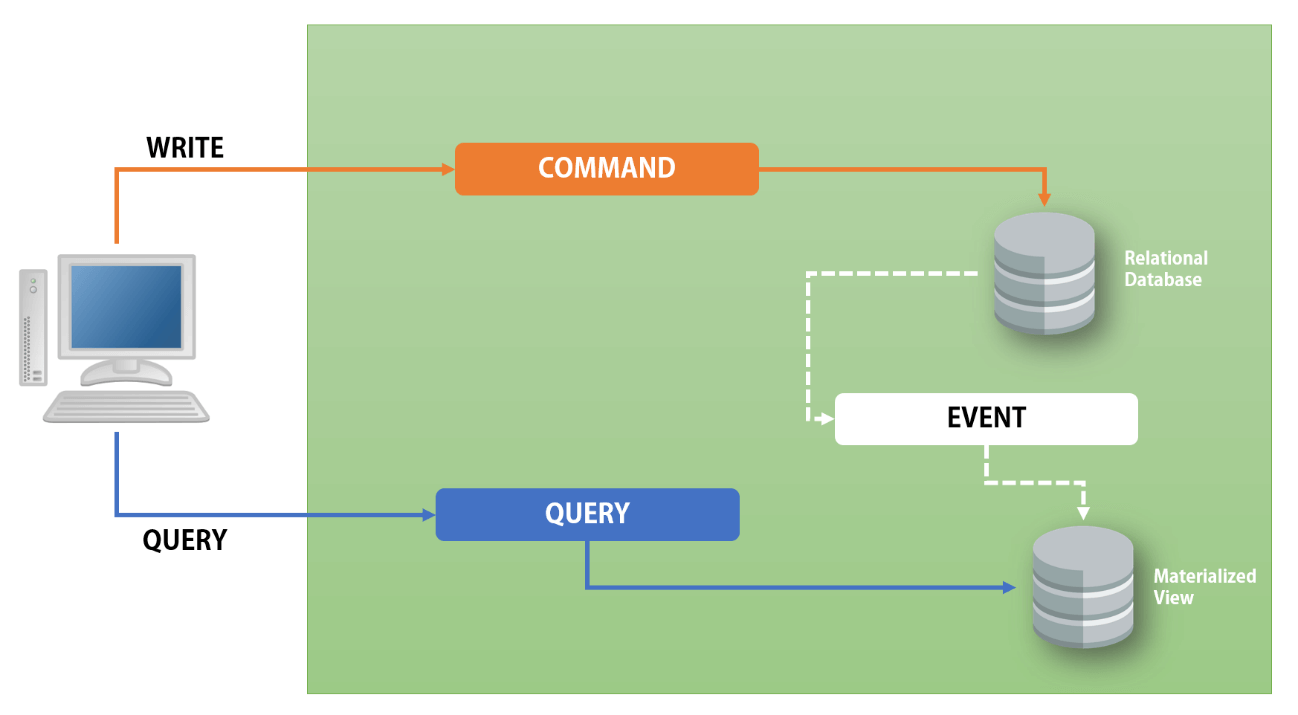
CQRS can be applied to a variety of applications, from simple web applications to complex enterprise systems. One common use case for CQRS is in event-driven architectures, where the application processes a large volume of events and must respond to them quickly and efficiently.
Another benefit of CQRS is that it can improve flexibility and fault tolerance. Since the read and write operations are separate, the program can continue to run even if one of the models fails. This feature can be important in critical applications where failure can have serious consequences.
CQRS can also be used to improve the user experience of an application. By optimizing the reading model for fast data retrieval, the application can respond to user requests quickly and provide a more interactive and responsive user interface. In addition, by separating the read and write operations, the application can ensure that the write operation does not interfere with the data read, and the overall performance and reliability of the application is increased.
Despite the challenges associated with implementing CQRS, many developers find it a valuable design pattern for building scalable, efficient, and maintainable applications. By separating read and write operations, CQRS can improve the performance, flexibility, and user experience of an application while simplifying its overall architecture. However, it can increase development time. But the long-term benefits of CQRS can make it a valuable feature for many applications.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment