
Cassandra database is a distributed NoSQL database that is used to manage a large amount of data on multiple servers. The main reasons for the popularity of this database are its high fault tolerance and accessibility. This database was developed in Facebook and is currently being used in major platforms such as Instagram, Twitter, Netflix and eBay.
Cassandra database design is based on scalability. Therefore, it will be easy to manage a large amount of data in a distributed manner. Also, due to the duplication of data in different nodes, the problems of accessibility and the failure of part of the data will be eradicated. . If one of the nodes becomes unavailable, the other nodes compensate for its task.
If all nodes in a particular segment of data go out of service, the data in that segment is temporarily unavailable until at least one node in the cluster containing the data comes back online.
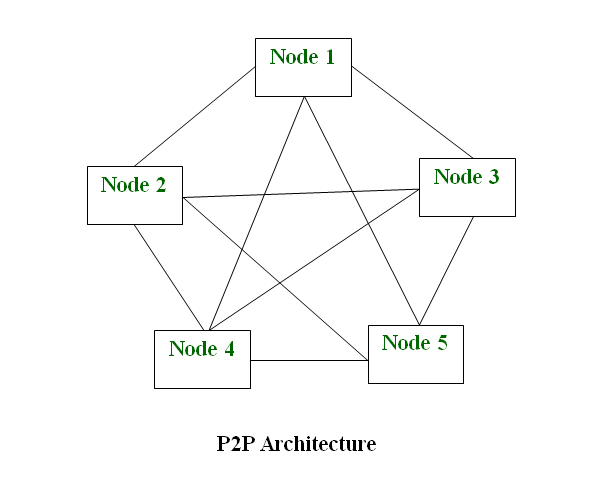
Cassandra does not have a central node or master node that connects all nodes in the cluster. Instead, Cassandra uses a decentralized peer-to-peer architecture where all cluster nodes communicate directly with each other without the need for a central node.
This decentralized architecture provides several advantages over a centralized architecture with a central node, including improved fault tolerance, better scalability, and more efficient communication between nodes. It also solves the bottleneck problem in the system.
In Cassandra, keyspaces are a namespace for tables. Keyspaces are similar to databases in relational database systems and are used to group related tables together.
When you create a keyspace, you can specify various properties such as replication strategy and replication factor. The replication strategy determines how data is replicated across multiple nodes in the cluster, while the replication factor specifies how many copies of each piece of data should be stored in the cluster for fault tolerance and availability.
Each keyspace can contain one or more tables, which are the main units of data storage in Cassandra. Tables in Cassandra have no defined structure, which means they can have a flexible structure that can be changed at any time without affecting the data stored in the table.

To access the Cassandra terminal, you can use the cqlsh command line tool that is installed on the system along with the Cassandra installation. Note that before running the cqlsh command, the Cassandra server must be running.
Cassandra uses a query language called CQL (Cassandra Query Language), which is very similar to SQL. Following are some common CQL commands that can be used to interact with a Cassandra database:
Create keyspace:
CREATE KEYSPACE <keyspace_name> WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': <replication_factor>};
CREATE KEYSPACE mykeyspace WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': 3};Use keyspace:
USE <keyspace_name>;
USE mykeyspace;Create Table:
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (<column1_name> <column1_type>, <column2_name> <column2_type>, ..., PRIMARY KEY (<partition_key_column_name>, <clustering_column_name>));
CREATE TABLE users (id UUID, name text, email text, PRIMARY KEY (id));Insert Data:
INSERT INTO <table_name> (<column1_name>, <column2_name>, ...) VALUES (<value1>, <value2>, ...);
INSERT INTO users (id, name, email) VALUES (c812a807-7a3c-4813-986d-817e132ae1b2, 'John Doe', 'john.doe@example.com');Reading data from the table along with the query:
SELECT <column1_name>, <column2_name>, ... FROM <table_name> WHERE <condition>;
SELECT name, email FROM users WHERE id = c812a807-7a3c-4813-986d-817e132ae1b2;Changing existing data:
UPDATE <table_name> SET <column1_name> = <new_value1>, <column2_name> = <new_value2>, ... WHERE <condition>;
UPDATE users SET email = 'jane.doe@example.com' WHERE id = c812a807-7a3c-4813-986d-817e132ae1b2;Delete data from table:
DELETE FROM <table_name> WHERE <condition>;
DELETE FROM users WHERE id = c812a807-7a3c-4813-986d-817e132ae1b2;
Note that these commands are only examples and may vary depending on your version of Cassandra.
To connect to a Cassandra database, like any other database, we need to create a connection string that specifies the IP address or domain name of one or more nodes along with authentication information.
The following are some examples of connection strings that can be used to connect to a Cassandra database:
Connecting to a node with the default port:
cassandra://<host_ip_address>/Connect to a node with a custom port:
cassandra://<host_ip_address:<port>/Connecting to a cluster with several nodes:
cassandra://<host1_ip_address>,<host2_ip_address>,<host3_ip_address>/Connecting with authentication:
cassandra://<username>:<password>@<host_ip_address>/Note that the exact syntax of the connection string may vary depending on the Cassandra driver or library used.
To read more about Cassandra and view the official documentation, you can use its official site at cassandra.apache.org

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment