In the world of computing, scaling is the process of adding more resources to an existing system to handle increased demand. This can be achieved through two methods: vertical scaling and horizontal scaling. In this article, we will examine the differences between vertical and horizontal scaling and the conditions under which each method is appropriate.
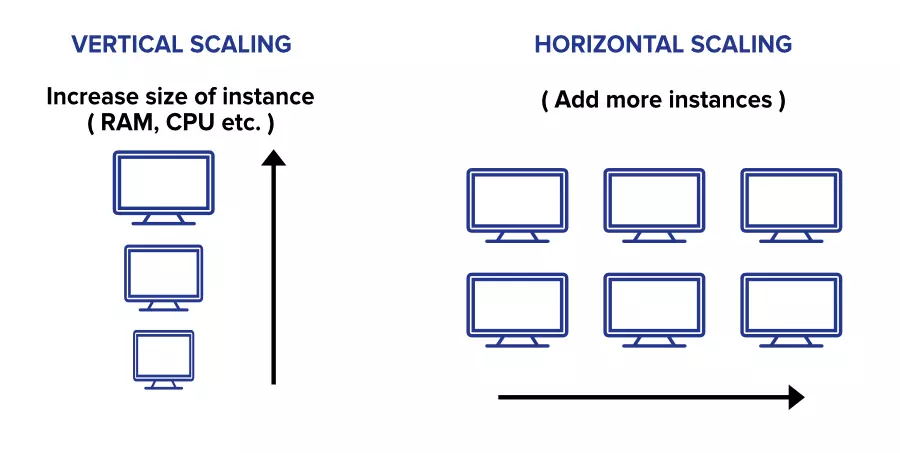
Vertical scaling involves adding more resources to an existing system by upgrading hardware. This can include adding more RAM, CPU, or disk space to an existing server. In essence, vertical scaling is like upgrading a computer by adding more processing resources.
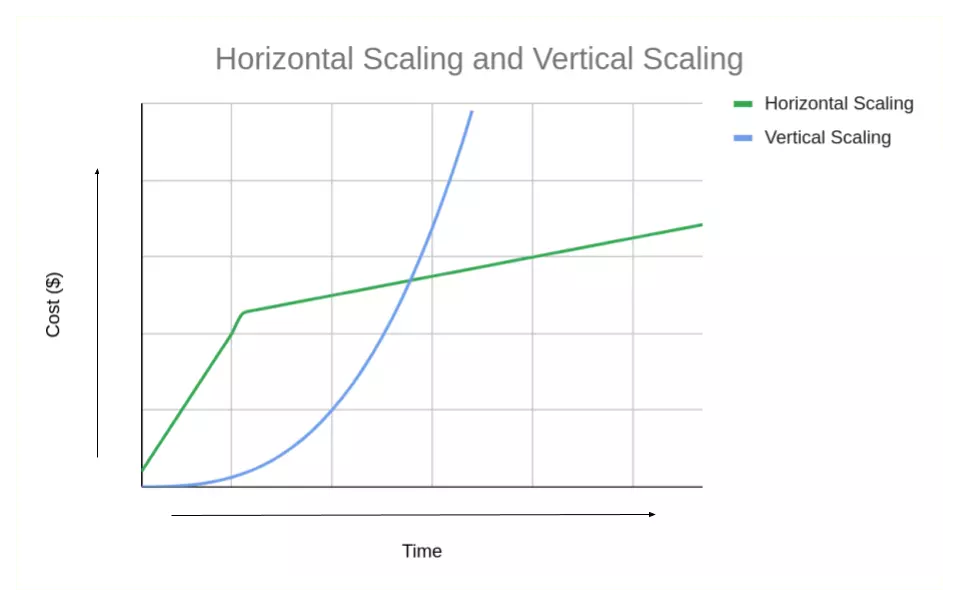
The main advantage of vertical scaling is that it is simple and fast. This does not require any changes to the software or system architecture, meaning the system can continue to operate normally. In addition, vertical scaling is usually less expensive than horizontal scaling because it does not require additional hardware and software designs.
However, vertical scaling has its drawbacks. In vertical scaling, there are limitations to increase the power of a system. When the hardware upgrade reaches its maximum capacity, scaling is no longer possible. Also, vertical scaling can have challenges because hardware upgrades can cause crashes and mess up system configurations.
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to the network. Horizontal scaling can include adding more servers to a load balancer, replicating databases and storing data on multiple servers, or distributing requests across multiple servers using a messaging queue.
The main advantage of horizontal scaling is that it is infinitely scalable. As long as enough servers are available, a system can continue to scale horizontally. Additionally, horizontal scaling can be more fault tolerant because if one server goes down, the others can continue to operate. For this reason, horizontal scaling is useful for websites and services with high traffic or applications that need to handle a large volume of requests.
However, horizontal scaling also has its drawbacks. First, its implementation can be complex, as it requires changes in software and system architecture. In addition, horizontal scaling can be more expensive than vertical scaling because it requires additional hardware and software designs.
There are several different architectures and approaches for horizontal scaling, which we briefly review below:
Load balancer: This is the most common approach for horizontal scaling. This method involves using a load balancer to distribute requests across multiple servers. Each server can handle a portion of requests, and if one server fails, the load balancer can redirect requests to other servers.
Microservices: Microservices are small, independent services that work together to form a larger application. Each microservice can be independently scaled horizontally, which enables greater flexibility and scalability. This approach can be more complex than traditional monolithic architectures, but offers greater flexibility and scalability.
Serverless: Serverless architecture includes the use of cloud solutions to handle system requests. The cloud provider handles system scaling automatically, which can simplify the horizontal scaling process. This approach can be more cost-effective than traditional server-based architectures, but it also requires a different approach to designing and deploying applications.
Containerization: This approach involves creating packages that contain our software and all its dependencies. These lightweight packages are capable of rapid deployment on container systems like Docker. Containers can be deployed on multiple servers and managed using container orchestration tools such as Kubernetes. This approach can provide greater flexibility and scalability than traditional virtual machine-based architectures.
Distributed Data: Distributed data storage involves replicating data across multiple servers to ensure that data is available and consistent across all servers. This approach can be done using technologies such as sharding, replication and NoSQL databases. This approach can be essential for applications that require high availability and fault tolerance. Cassandra and CockroachDB databases are used in large and distributed systems.
There are different approaches for horizontal scaling, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. Factors such as scalability, flexibility, cost, and complexity should be considered when deciding to use these approaches. By choosing the right architecture and approach for your application, you can ensure that your system has the ability to handle incoming requests and provide a good user experience.
Vertical and horizontal scaling both have their advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right method depends on the specific needs of the system. Vertical scaling is simpler and less expensive, but it has limitations. Horizontal scaling is more complex and expensive, but infinitely scalable and provides high availability and fault tolerance. By understanding the differences between vertical and horizontal scaling, you can make an informed decision about which scaling method to use for your system.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment