
In web services, a variety of cache methods are used to increase the speed of receiving information by the user. Different types of these methods are used based on the different needs of the system. In this article, different cache levels and their application are presented.
Client-side caching is a technique for storing data on the user's device (such as browser cache), which helps to reduce the number of requests sent to the server. This technique is useful for static resources such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files that are used on multiple different pages. When a user visits a website that uses client-side caching, the browser caches the resources needed to load the page. The next time a user visits a website, the browser first checks the available caches for the required resources before requesting them from the server. This action helps to reduce the load on the server and improve the performance of the application.
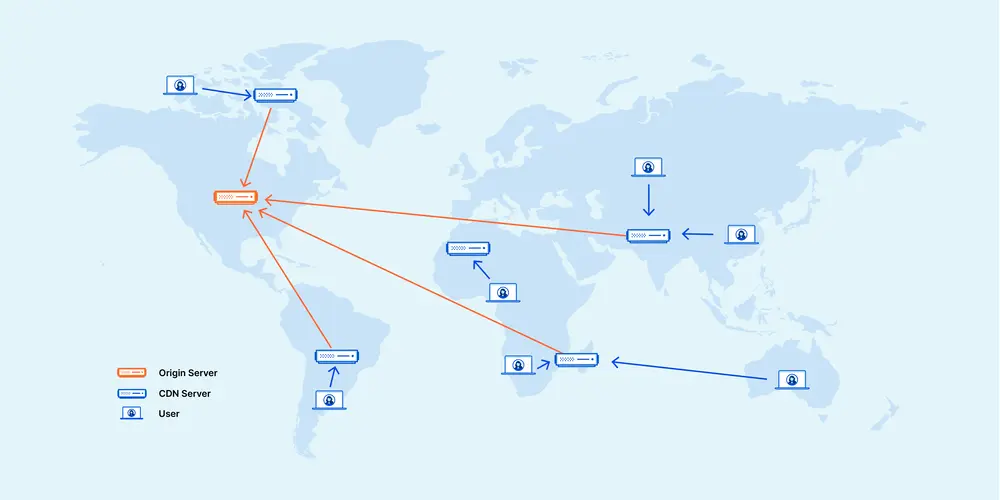
CDN cache is a type of cache that stores the content required by the user on servers that are geographically close to the user. This makes the time to deliver the content to the user significantly reduced, because the request is served from the nearby server instead of the main server. A CDN cache is useful for serving static resources such as images, videos, and other multimedia content. When a request for content is made, the CDN first checks its cache for the content. If the content exists in the cache, it is served from the cache server, which reduces the load on the origin server and improves application performance. The most popular and largest provider of this service is Cloudflare, which has made this service available with various plans, including the free plan.
Server-side caching involves storing data that can be accessed on the server side and reduces the number of requests sent to databases. This type of cache is especially useful for dynamic data that is used frequently. When the request is made, the program first checks if the data exists in the cache. If the data exists in the cache, it is returned to the user and there is no need to call the database and read the data from the disk. This practice can significantly reduce the response time for frequently called data and improve application performance.
Database caching is a technique to store frequently used data in RAM memory in order to reduce the number of times the database needs to call them from disk. This technique can improve application performance by reducing the time it takes to retrieve data from the database. When an application requests information from the database, it is first checked in the cache. If the data exists in the cache, it is returned to the application and there is no need to query the database. Common tools for using database cache are Redis, Memcached, Oracle Coherence, Hazelcast, Couchbase.

Distributed storage involves storing data on multiple servers to improve performance and data availability. This practice is often used in large-scale applications with high levels of traffic. When a request for data is received, the cache layer first checks whether the data is available in the local cache. If the data does not exist in the local cache, it is retrieved from a remote cache node. This type of cache can significantly reduce the load on the database and improve application performance, especially in distributed environments. Common tools for implementing this type of cache are Hazelcast, Apache Ignite, Redis Cluster.
The importance of each cache layer varies depending on the needs and design of the service.
A client-side cache is useful for improving the performance of websites and reducing the load on the server, especially for static resources that are commonly used on multiple pages.
CDN caching can be critical to quickly serving content to users, especially for large-scale applications that serve content to users around the world.
Server-side cache and database cache are both important for improving the performance of dynamic applications, especially for data that is frequently called.
Distributed caching can be important for large-scale, distributed applications with high levels of traffic, as it can significantly reduce the load on the database and improve application performance.
Therefore, each cache layer is important in its own way and the choice of the policy of using different types of caches depends on the needs and the way the system is designed.

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment