
In microservices architecture, Gateway is the layer between clients and microservices. The main role of a Gateway is to direct client requests to appropriate microservices and implement processes such as authentication, authorization, rate limiting, etc.
The Gateway layer acts as a central entry point into microservices applications. This means that client software can communicate with microservices through an endpoint, which simplifies the overall communication process. When all communication is done through a single interface, you can be sure about the authentication, authorization and integrity of system.
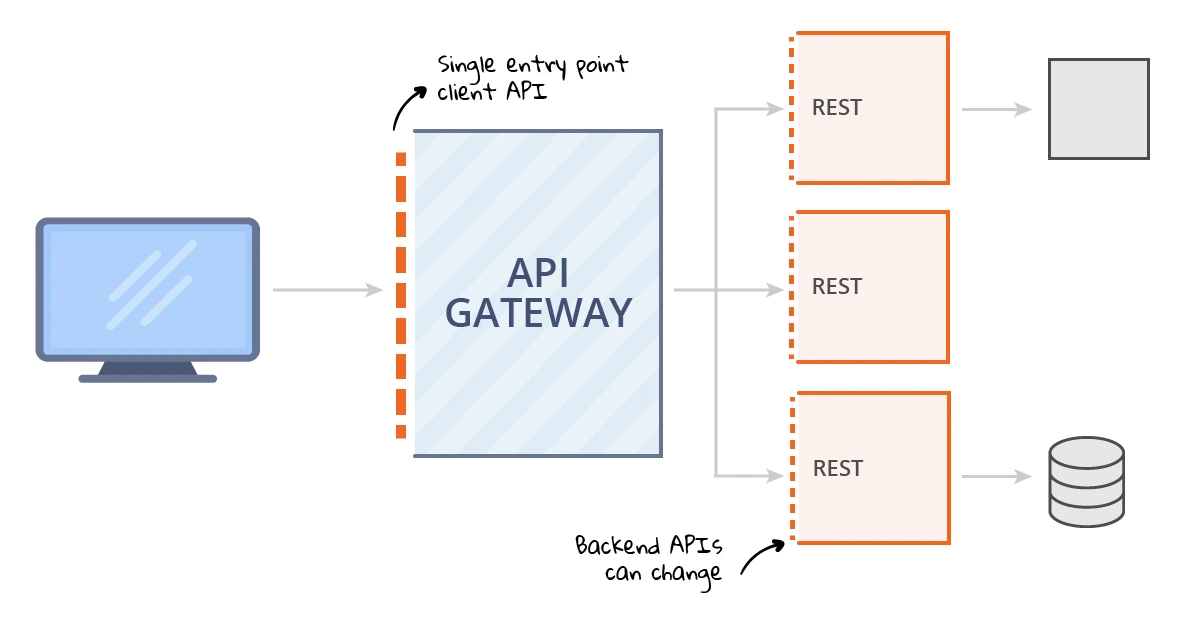
Microservices can be implemented using different programming languages and run on different servers or containers. API Gateway simplifies the complexities of using several different services and provides a unified API to the client. Therefore, the client program will not be involved in the implementation of these complications.
If the Gateway is not properly designed and implemented, it can become a bottleneck. In a microservice architecture, the API Gateway is a central component that handles all requests received from users and sends them to the appropriate microservice. If the API Gateway is not scalable, it can become a bottleneck, causing response delays and affecting overall system performance.
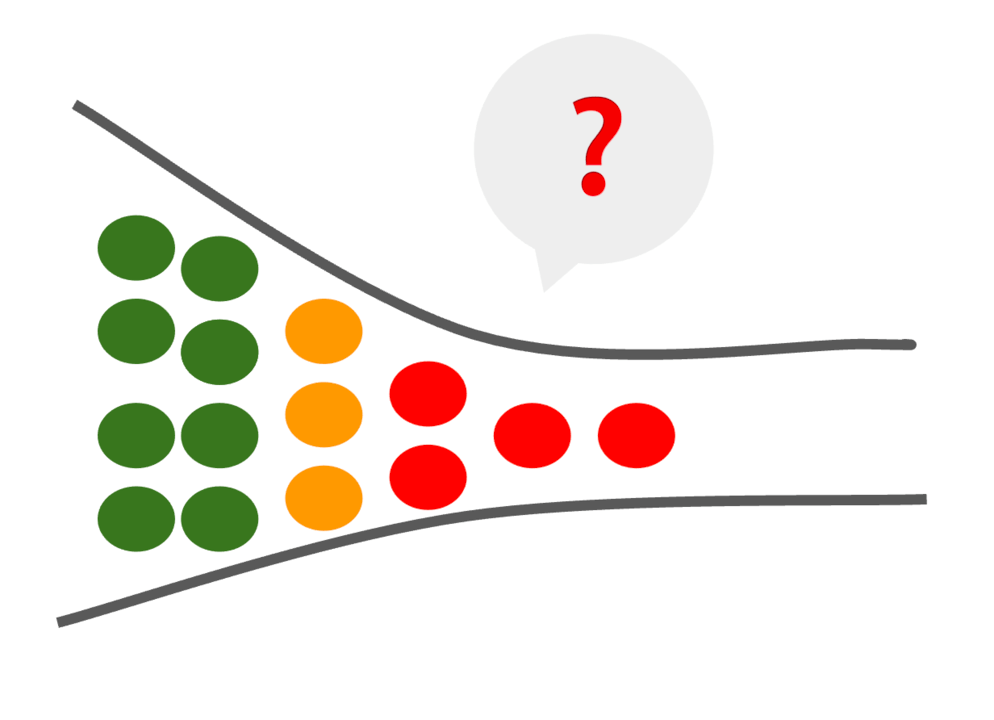
However, there are several ways to avoid this bottleneck. One approach is to use horizontal scaling, which involves deploying multiple Gateway instances and distributing incoming traffic among them. Another method is to use cache and content delivery networks (CDN) to reduce the load.
In addition, code optimization and correct implementation of microservices architecture can also help reduce the load on the Gateway. For example, by implementing efficient and optimized microservices, as well as using asynchronous messaging, the amount of processing required by the API Gateway can be reduced, allowing it to handle more requests without becoming a bottleneck.
Communication between API Gateway and microservices can be synchronous or asynchronous. In synchronous communication, API Gateway waits for a response from the microservice before returning the response to the client. In asynchronous communication, API Gateway puts a message in the processing queue and continues to process other requests without waiting. In order for communication between Gateway and services to be managed and reliable, error handling and retry mechanisms must be properly implemented. If all these things are taken into consideration and their correct implementation, it can be ensured that the system works properly and will be scalable.
If we want to list the important points about API Gateway, this list will be as follows:

I am Reza Babakhani, a software developer. Here I write my experiences, opinions and suggestions about technology. I hope that what I write is useful for you.
leave a comment